Parkinson’s disease
Parkinson's disease is a disorder of the brain that leads to shaking (tremors) and difficulty with walking, movement, and coordination.
CAUSES
Parkinson's disease most often develops after age 50. It is one of the most common nervous system disorders of the elderly. Sometimes Parkinson's disease occurs in younger adults. It affects both men and women.
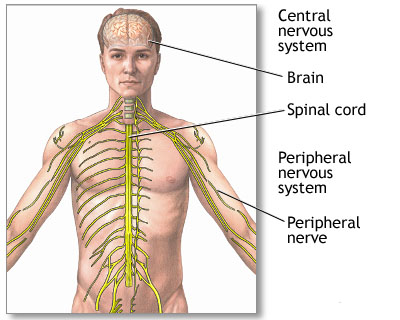
The central nervous system is comprised of the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system includes all peripheral nerves.
In some cases, Parkinson's disease runs in families. When a young person is affected, it is usually because of a form of the disease that runs in families.
Nerve cells use a brain chemical called dopamine to help control muscle movement. Parkinson's disease occurs when the nerve cells in the brain that make dopamine are slowly destroyed. Without dopamine, the nerve cells in that part of the brain cannot properly send messages. This leads to the loss of muscle function. The damage gets worse with time. Exactly why these brain cells waste away is unknown.
Parkinson's is rare in children. It may occur because the nerves are not as sensitive to dopamine.
The term "parkinsonism" refers to any condition that involves the types of movement changes seen in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism may be caused by other disorders (called secondary parkinsonism) or certain medications.
SYMPTOMS
Symptoms may be mild at first. For instance, you may have a mild tremor or a slight feeling that one leg or foot is stiff and dragging. Symptoms may affect one or both sides of the body, and can include:
Symptoms include:
- Slow blinking
- Constipation
- Difficulty swallowing
- Drooling
- Problems with balance and walking
- No expression in the face (like you are wearing a mask)
- Muscle aches and pains
Movement problems, which include:
- Difficulty starting movement, such as starting to walk or getting out of a chair
- Difficulty continuing to move
- Slowed movements
- Loss of small or fine hand movements; writing may become small and difficult to read; eating becomes difficults
- Rigid or stiff muscles, often beginning in the legs
- Shaking, called tremors
- Usually occurs in the limbs at rest, or when the arm or leg is held out
- Goes away when you move
- Eventually may be seen in the head, lips, tongue, and feet
- May be worse when tired, excited, or stressed
- Finger-thumb rubbing (pill-rolling tremor) may be present
- Slowed, quieter speech and monotone voice
- Stooped position
Low blood pressure when getting up, sweating, drooling, lack of body temperature control. These problems are due to something called autonomic dysfunction.
Other symptoms may include:
- Anxiety, stress, and tension
- Confusion
- Dementia
- Depression
- Fainting
- Hallucinations
- Memory loss
EXAMS AND TESTS
Your health care provider may be able to diagnose Parkinson's disease based on your symptoms and a physical examination. However, the symptoms can be difficult to assess, particularly in the elderly. They become more clear as the illness gets worse.
A doctor's examination may show:
- Difficulty starting or finishing voluntary movements
- Jerky, stiff movements
- Muscle atrophy
- Shaking (tremors)
- Changes in your heart rate
- Reflexes should be normal.
Tests may be needed to rule out other disorders that cause similar symptoms.
TREATMENT
There is no known cure for Parkinson's disease. The goal of treatment is to control symptoms.
Medications control symptoms, mostly by increasing the levels of dopamine in the brain. At certain points during the day, the helpful effects of the medication often wears off, and symptoms can return. If this happens to you, your health care provider may need to change the:
- Type of medication
- Dose
- Amount of time between doses
- How the medicine is taken
Work closely with your doctors and therapists to find a treatment program that works best for you. Never change or stop taking any medications without talking with your doctor.
Many medications can cause severe side effects, including hallucinations, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and delirium. Monitoring and follow-up by the health care provider is important.
Eventually, symptoms such as stooped posture, frozen movements, and speech difficulties may not respond very well to drug treatment.
Medications used to treat movement-related symptoms of Parkinson's disease include:
- Levodopa (L-dopa), Sinemet, levodopa and carbidopa (Atamet)
- Pramipexole (Mirapex), ropinirole (Requip), bromocriptine (Parlodel)
- Selegiline (Eldepryl, Deprenyl), rasagiline (Azilect)
- Amantadine or anticholinergic medications to reduce early or mild tremors
- Entacapone
Other medications may include:
- Memantine, rivastigmine, galantamine for cognitive difficulties
- Antidepressants for mood disorders
- Gabapentin, duloxetine for pain
- Fludrocortisone, midodrine, botox, sidenafil for autonomic dysfunction
- Armodafinil, clonazepam, zolpidem for sleep disorders
Lifestyle changes may be helpful for Parkinson's disease:
Good general nutrition and health. Changes in what you eat or drink are needed if there are swallowing problems
Exercising, but adjusting the activity level to meet changing energy levels
Regular rest periods and avoiding stress
Physical therapy, speech therapy, and occupational therapy
Railings or banisters placed in commonly used areas of the house. Other changes may be needed around the home to prevent falls and make the bathroom safe.
Assistive devices, such as special eating utensils, wheelchairs, bed lifts, shower chairs, walkers, and wall bars
Social workers or other counseling services to help you cope with the disorder and get assistance (such as Meals-on-Wheels)
Surgery may be an option for some patients with Parkinson's disease. These surgeries do not cure Parkinson's, but may help ease symptoms.
Deep brain stimulation involves placing electrical stimulators in specific areas of the brain that control movement.
Another type of surgery destroys brain issues that cause Parkinson's symptoms.
Stem cell transplant and other clinical trials are currently ongoing in the USA. For information, see: www.pdtrials.org
OUTLOOK (PROGNOSIS)
Untreated, the disorder will get worse until a person is totally disabled. Parkinson's may lead to a deterioration of all brain functions, and an early death.
Most people respond to medications. How much the medications relieve symptoms, and for how long can be very different in each person. The side effects of medications may be severe.
POSSIBLE COMPLICATIONS
- Difficulty performing daily activities
- Difficulty swallowing or eating
- Disability (differs from person to person)
- Injuries from falls
- Pneumonia from breathing in (aspirating) saliva
- Side effects of medications
WHEN TO CONTACT A MEDICAL PROFESSIONAL
Call your health care provider if:
- You have symptoms of Parkinson's disease
- Symptoms get worse
- New symptoms occur
Also tell the health care provider about medication side effects, which may include:
- Changes in alertness, behavior or mood
- Delusional behavior
- Dizziness
- Hallucinations
- Involuntary movements
- Loss of mental functions
- Nausea and vomiting
- Severe confusion or disorientation
Also call your health care provider if the condition gets worse and home care is no longer possible.
Source: http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000755.htm


 Общие симптомы
Общие симптомы  Голова, зрение, слух, речь
Голова, зрение, слух, речь  Шея и горло
Шея и горло  Грудь, сердце и дыхание
Грудь, сердце и дыхание  Живот, желудок, кишечник
Живот, желудок, кишечник  Конечности, суставы, спина, поясница
Конечности, суставы, спина, поясница  Таз, мочеполовые органы
Таз, мочеполовые органы  Наружные поверхности, кожа, волосы
Наружные поверхности, кожа, волосы