Myopia
What is myopia?
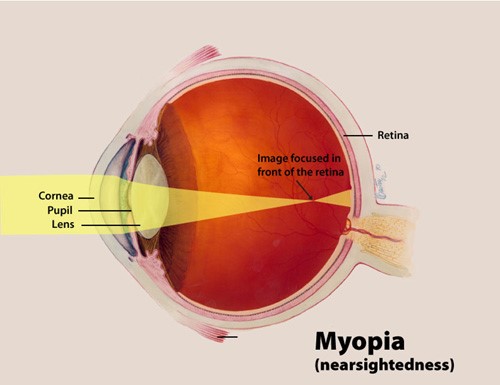
Myopia, also known as nearsightedness, is a common type of refractive error where close objects appear clearly, but distant objects appear blurry.
What is high myopia?
High myopia is a severe form of the condition. In high myopia, the eyeball stretches and becomes too long. This can lead to holes or tears in the retina and can also cause retinal detachment. Abnormal blood vessels may grow under the retina and cause changes in vision. People with high myopia need comprehensive dilated eye exams more often. Early detection and timely treatment can help prevent vision loss.
What is refraction?
Refraction is the bending of light as it passes through one object to another. Vision occurs when light rays are bent (refracted) as they pass through the cornea and the lens. The light is then focused on the retina. The retina converts the light-rays into messages that are sent through the optic nerve to the brain. The brain interprets these messages into the images we see.
What are refractive errors?
In refractive errors, the shape of the eye prevents light from focusing on the retina. The length of the eyeball (longer or shorter), changes in the shape of the cornea, or aging of the lens can cause refractive errors.
Causes and Risk Factors
How does myopia develop?
Myopia develops in eyes that focus images in front of the retina instead of on the retina, which results in blurred vision. This occurs when the eyeball becomes too long and prevents incoming light from focusing directly on the retina. It may also be caused by an abnormal shape of the cornea or lens.
Who is at risk for myopia?
Myopia can affect both children and adults. The condition affects about 25 percent of Americans. Myopia is often diagnosed in children between 8 and 12 years of age and may worsen during the teen years. Little change may occur between ages 20 to 40, but sometimes myopia may worsen with age. People whose parents have myopia may be more likely to get the condition.
Symptoms and Detection
What are the signs and symptoms of myopia?
Some of the signs and symptoms of myopia include:
- Headaches
- Eyestrain
- Squinting
- Difficulty seeing distant objects, such as highway signs
How is myopia diagnosed?
An eye care professional can diagnose myopia and other refractive errors during a comprehensive dilated eye examination. People with this condition often visit their eye care professional with complaints of visual discomfort or blurred vision
Treatment
How is myopia corrected?
Myopia can be corrected with eyeglasses, contact lenses, or surgery.
Eyeglasses are the simplest and safest way to correct myopia. Your eye care professional can prescribe lenses that will correct the problem and help you to see your best.
Contact Lenses work by becoming the first refractive surface for light rays entering the eye, causing a more precise refraction or focus. In many cases, contact lenses provide clearer vision, a wider field of vision, and greater comfort. They are a safe and effective option if fitted and used properly. However, contact lenses are not right for everyone. Discuss this with your eye care professional.
Refractive Surgery aims to permanently change the shape of the cornea which will improve refractive vision. Surgery can decrease or eliminate dependency on wearing eyeglasses and contact lenses. There are many types of refractive surgeries and surgical options should be discussed with an eye care professional.


 Общие симптомы
Общие симптомы  Голова, зрение, слух, речь
Голова, зрение, слух, речь  Шея и горло
Шея и горло  Грудь, сердце и дыхание
Грудь, сердце и дыхание  Живот, желудок, кишечник
Живот, желудок, кишечник  Конечности, суставы, спина, поясница
Конечности, суставы, спина, поясница  Таз, мочеполовые органы
Таз, мочеполовые органы  Наружные поверхности, кожа, волосы
Наружные поверхности, кожа, волосы