Lyme disease
Lyme disease is a bacterial infection that is spread through the bite of one of several types of ticks.
Causes
Lyme disease is caused by bacteria called Borrelia burgdorferi (B. burgdorferi).
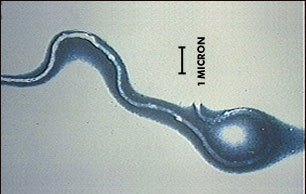
Fig 1:Borrelia burgdorferi is a spirochete bacteria that causes Lyme disease. It is similar in shape to the spirochetes that cause other diseases, such as relapsing fever and syphilis
Blacklegged ticks and other species of ticks can carry these bacteria. The ticks pick up the bacteria when they bite mice or deer that are infected with B. burgdorferi. You can get the disease if you are bitten by an infected tick.
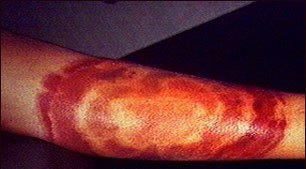
Fig: Erythema chronicum migrans is the initial lesion of Lyme disease, and often appears at the site of the infecting tick bite. It is a red, enlarging rash, flat or slightly raised, and may reach from 4 to 20 inches across
There are 3 stages of Lyme disease.
- Stage 1 is called early localized Lyme disease. The infection has not yet spread throughout the body.
- Stage 2 is called early disseminated Lyme disease. The bacteria have begun to spread throughout the body.
- Stage 3 is called late disseminated Lyme disease. The bacteria have spread throughout the body.
Risk factors for Lyme disease include:
- Doing outside activities that increase tick exposure (for example, gardening, hunting, or hiking) in an area where Lyme disease is known to occur
- Having a pet that may carry ticks home
- Walking in high grasses
Important facts about tick bites and Lyme disease:
- In most cases., a tick must be attached to your body within 36 hours to spread the bacteria to your blood.
- Blacklegged ticks can be so small that they are almost impossible to see. Many people with Lyme disease never even see or feel a tick on their body.
- Most people who are bitten by a tick do not get Lyme disease.
Symptoms
Symptoms of early localized Lyme disease (stage 1) begin days or weeks after infection. They are similar to the flu and may include:
- Chills
- Fever
- General ill feeling
- Headache
- Joint pain
- Muscle pain
- Stiff neck
There may be a "bull's eye" rash, a flat or slightly raised red spot at the site of the tick bite. Often there is a clear area in the center. It can be large and expanding in size. This rash is called erythema migrans. Without treatment, it can last 4 weeks or longer.
Symptoms may come and go. Untreated, Lyme disease can spread to the brain, heart, and joints.
Symptoms of early disseminated Lyme disease (stage 2) may occur weeks to months after the tick bite, and may include:
- Numbness or pain in the nerve area
- Paralysis or weakness in the muscles of the face
- Heart problems, such as skipped heartbeats (palpitations), chest pain, or shortness of breath
Symptoms of late disseminated Lyme disease (stage 3) can occur months or years after the infection. The most common symptoms are muscle and joint pain. Other symptoms may include:
- Abnormal muscle movement
- Joint swelling
- Muscle weakness
- Numbness and tingling
- Speech problems
- Thinking (cognitive) problems
Exams and Tests
A blood test can be done to check for antibodies to the bacteria that cause Lyme disease. The most commonly used is the ELISA for Lyme disease test. An immunoblot test is done to confirm ELISA results. Be aware, though, in the early stage of infection, blood tests may be normal.
In areas where Lyme disease is more common, your health care provider may be able to diagnose early disseminated Lyme disease (Stage 2) without doing any lab tests.
Other tests that may be done when the infection has spread include:
- Electrocardiogram
- Echocardiogram to look at the heart
- MRI of the brain
- Spinal tap (lumbar puncture to examine spinal fluid
Treatment
Persons bitten by a tick should be watched closely for at least 30 days to see if a rash or symptoms develop.
A single dose of the antibiotic doxycycline may be given to someone soon after being bitten by a tick, when all of these conditions are true:
- The person has a tick that can carry Lyme disease attached to his or her body. This usually means that a nurse or doctor has looked at and identified the tick.
- The tick is thought to have been attached to the person for at least 36 hours.
- The person is able to start taking the antibiotic within 72 hours of removing the tick.
- The person is 8 years or older and is not pregnant or breastfeeding.
- Local rate of ticks carrying B. burgdorferi is 20 percent or higher.
A 10 day to 4-week course of antibiotics is used to treat people who are diagnosed with Lyme disease, depending on the choice of drug:
- The choice of antibiotic depends on the stage of the disease and the symptoms.
- Common choices include doxycycline, amoxicillin, azithromycin, cefuroxime, and ceftriaxone.
Pain medicines, such as ibuprofen, are sometimes prescribed for joint stiffness.
Outlook (Prognosis)
If diagnosed in the early stages, Lyme disease can be cured with antibiotics. Without treatment, complications involving the joints, heart, and nervous system can occur. But these symptoms are still treatable and curable.
In rare cases, a person keeps having symptoms that interfere with daily life after they have been treated with antibiotics. This is also known as post-Lyme disease syndrome. The cause of this syndrome is unknown.
Symptoms that occur after antibiotics are stopped may not be signs of active infection and may not respond to antibiotic treatment.
Possible Complications
Stage 3, or late disseminated, Lyme disease can cause long-term joint inflammation (Lyme arthritis) and heart rhythm problems. Brain and nervous system problems are also possible, and may include:
- Decreased concentration
- Memory disorders
- Nerve damage
- Numbness
- Pain
- Paralysis of the face muscles
- Sleep disorders
- Vision problems
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Call your health care provider if you have:
- A large, red, expanding rash that may look like a bull's eye.
- Had a tick bite and develop weakness, numbness, tingling, or heart problems.
- Symptoms of Lyme disease, especially if you may have been exposed to ticks.
Prevention
Take precautions to avoid tick bites. Be extra careful during warmer months. When possible, avoid walking or hiking in the woods and areas with high grass.
If you do walk or hike in these areas, take measures to prevent tick bites:
- Wear light-colored clothing so that if ticks land on you, they can be spotted and removed.
- Wear long sleeves and long pants with pant legs tucked into your socks.
- Spray exposed skin and your clothing with insect repellant.
- After returning home, remove your clothes and thoroughly inspect all skin surface areas, including your scalp. Shower as soon as possible to wash off any unseen ticks.
If a tick is attached to you, follow these steps to remove it:
- Grasp the tick close to its head or mouth with tweezers. Do not use your bare fingers. If needed, use a tissue or paper towel.
- Pull it straight out with a slow and steady motion. Avoid squeezing or crushing the tick. Be careful not to leave the head embedded in the skin.
- Clean the area thoroughly with soap and water. Also wash your hands thoroughly.
- Save the tick in a jar.
- Watch carefully for the next week or two for signs of Lyme disease.
- If all parts of the tick cannot be removed, get medical help. Bring the tick in the jar to your doctor appointment.
Source: http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/001319.htm
Lumps and Swelling (male | female)
General Skin Problems (male | female)
Painful Joints (female | male)
Rash with Fever (male | female)
Теги:


 Общие симптомы
Общие симптомы  Голова, зрение, слух, речь
Голова, зрение, слух, речь  Шея и горло
Шея и горло  Грудь, сердце и дыхание
Грудь, сердце и дыхание  Живот, желудок, кишечник
Живот, желудок, кишечник  Конечности, суставы, спина, поясница
Конечности, суставы, спина, поясница  Таз, мочеполовые органы
Таз, мочеполовые органы  Наружные поверхности, кожа, волосы
Наружные поверхности, кожа, волосы